A really good concept as a supporting framework for a strong partner network is the result of years of development work. Good and coherent, a
concept that makes it possible to use the DIR® system as a therapeutic link between dentistry and dental technology as well as complete planning
from the first impression to the finished restoration (planning reliability).
The range of indications for the DIR® concept includes both the prosthetic restoration of patients with CMD syndrome and the fabrication of new dentures for functionally healthy patients.
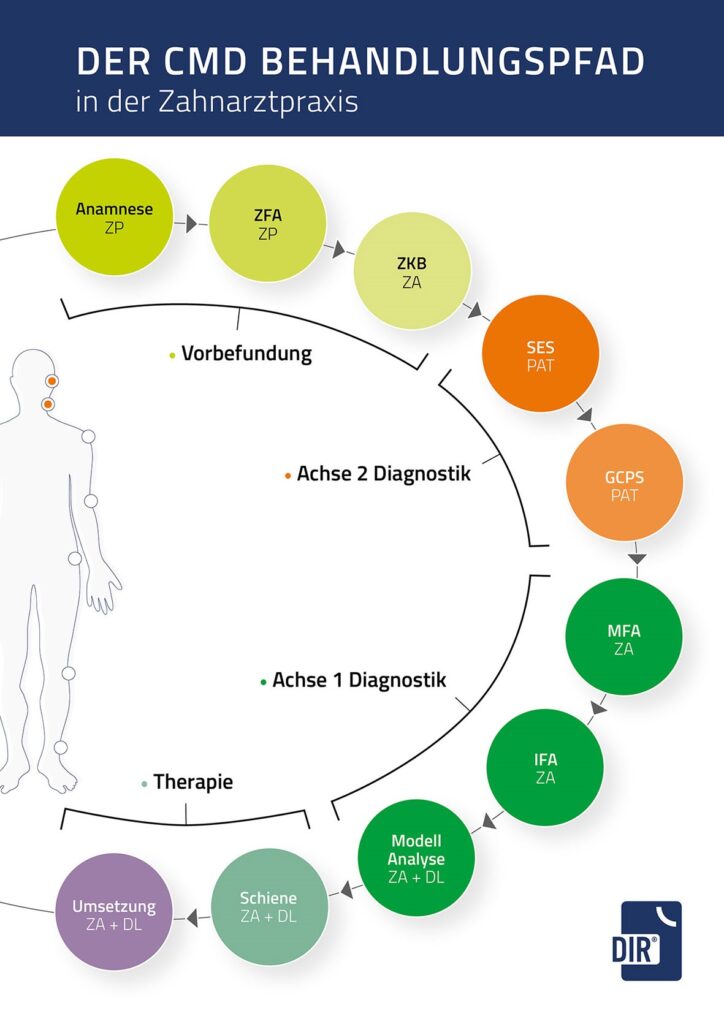
Diagnostics
As part of the DIR® concept, the FunktioCheck Pro® software documents the preliminary dental findings.
The type of complaints and previous visits to the dentist from other specialist disciplines are recorded as part of the functional dental history. In the brief dental findings, missing canine guidance, non-age-appropriate abrasion of the teeth in the sense of grinding facets and abrasions or The brief dental findings record missing canine guidance in the sense of grinding facets and abrasions or wedge-shaped incisions, tooth loosening, tilting and migration, gingival recessions with Still-man clefts and McCall’s garlands, pain during muscle palpation, temporomandibular joint noises as well as restrictions and asymmetrical mouth opening movements, resulting in a three-grade probability statement for the presence of a functional disorder and a recommendation for further findings.
Axis 2 diagnostics
The special functional analysis carried out in the case of a high probability of CMD, the so-called Axis 2 diagnostics, is highly relevant for the success of the subsequent therapy and is objectively assessed using a Graded Chronic Pain Scale and a pain perception scale, whereby an evaluation of the patient’s degree of psychological stress is possible in an evaluation form.
Manual-clinical diagnostics
The subsequent manual-clinical diagnostics allow an assessment of a manifest arthropathy with examination of the temporomandibular joint function to exclude or confirm the presence of a disc perforation or a disc displacement, condylar osteoarthrosis, hypermobility, capsulitis or inflammation of the bilaminar zone. The morphological or structural remodeling processes in the hard tissues should of course be confirmed radiologically (MRI). Manifest myopathy is assessed by performing standardized masticatory muscle examinations using the isometric tension test and muscle palpation.
Instrumental functional analysis
The manual functional analysis is followed by the instrumental functional analysis with the DIR® system, which is also carried out on functionally healthy patients as part of prosthetic planning. The electronic measuring method is based on the arrow angle or support pin registration according to Gerber with recording of the marginal movements of the mandible under physiological masticatory pressure and without reference to occlusion.
Centric position as target bite
Once the DIR® measurement has been completed, the centric position determined is encoded in the patient’s mouth as a so-called target bite by guiding the support pin into a fixation plate under defined chewing pressure. This is followed by transfer to the articulator. In the following model analysis, an occlusion analysis is performed, whereby the deviation of the habitual occlusion or the current actual state from the centric occlusion or the target bite is documented.
