Reliable DIR® diagnostics: Tracking down the functional disorder through intraoral
measurement!
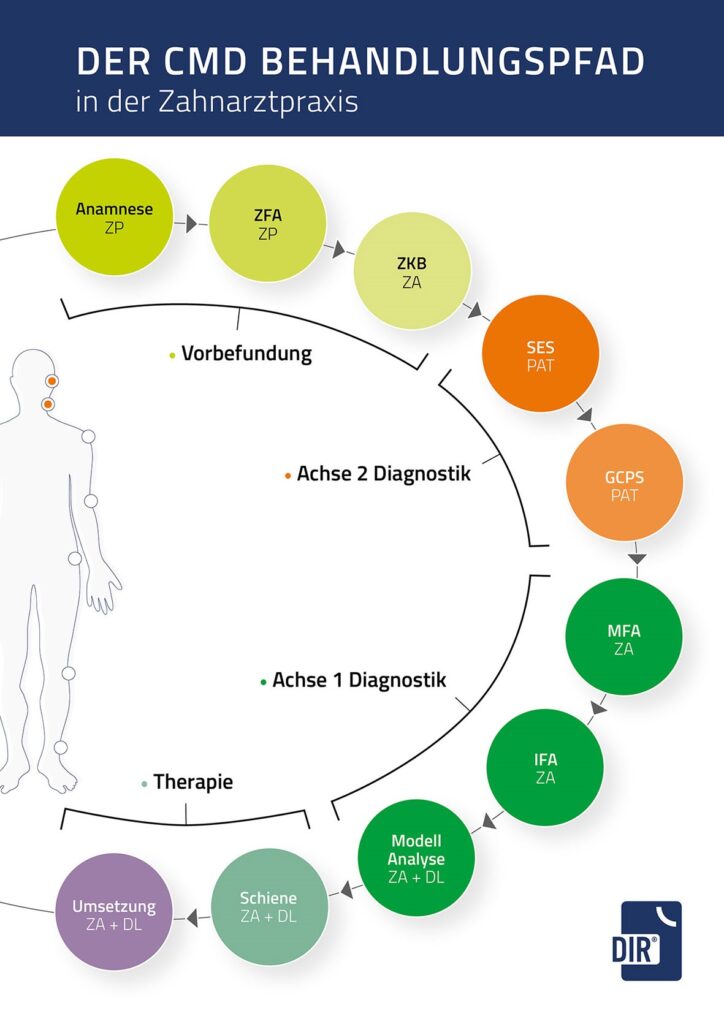
If a functional disorder is suspected – especially after a clinical functional analysis – dentists obtain definitive clarity about the individual situation of the craniomandibular system through further instrumental analysis. The centric condylar position, which is considered ideal for smooth functioning of the temporomandibular joint, is also determined.

Definition of centric condylar position
The cranioventral, not laterally displaced position of both condyles with physiologic condyle-discus relation and physiologic loading of the involved tissue structures (DGZMK and DGFDT)
“In the centric condylar position, both condyles are not laterally displaced in the cranioventral section of the eminentia if the vertical dimension of the mandible to the maxilla is correct.
In this circumscribed area, the tissues involved are not subjected to excessive pressure or tension.
There is freedom of movement in all three spatial directions.
The centric condylar position can be controlled and maintained neuromuscularly with minimal energetic effort.”
DIR® (DYNAMIC INTRAORAL REGISTRATION)
An intraoral measurement of the patient with the DIR® system enables the function of the craniomandibular system to be assessed.
A support pin register is used here, whereby the recording of the lower jaw movements is transferred to a medical PC in real time at any time via the DIR® System software and the dentist can observe the movements of the lower jaw. Recording and bite encoding take place under a defined chewing force. (ACTUAL POSITION)
The DIR® System software supports the dentist in converting the ACTUAL to TARGET position.
The physiological condyle position is the focus of the bite adjustment.
After evaluating the results, misalignments can be corrected and secured as part of the DIR® treatment concept, using the DIR® splint, among other things. It also serves to retrain the masticatory muscles. Only after correction and freedom from pain should dental treatment be continued and the TARGET POSITION reconstructed (e.g. with dentures).

Instrumental functional analysis with the DIR® system is used for
- Suspicion of CMD
- Setting the physiologically optimal bite position
- Fabrication of new dentures
- Orthodontic treatment
- Patients who were not treated according to the DIR® concept (e.g. with dentures) and now have complaints
- Bruxism, abrasive dentition, joint noises and other complaints
The high quality and safety of DIR® diagnostics is also guaranteed by regular training courses (refresher seminars, acquisition of current DIR® quality seals).