Centric position as target bite
After the DIR® measurement has been carried out in the dental practice, it is transferred to the articulator in a DIR® authorized dental laboratory.
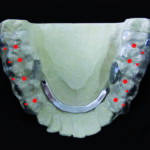
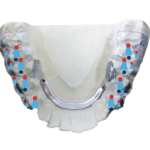
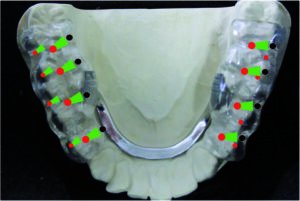
In the following model analysis, an occlusion analysis is performed, whereby the deviation of the habitual occlusion or the current ACTUAL state from the centric occlusion or the TARGET bite is documented.
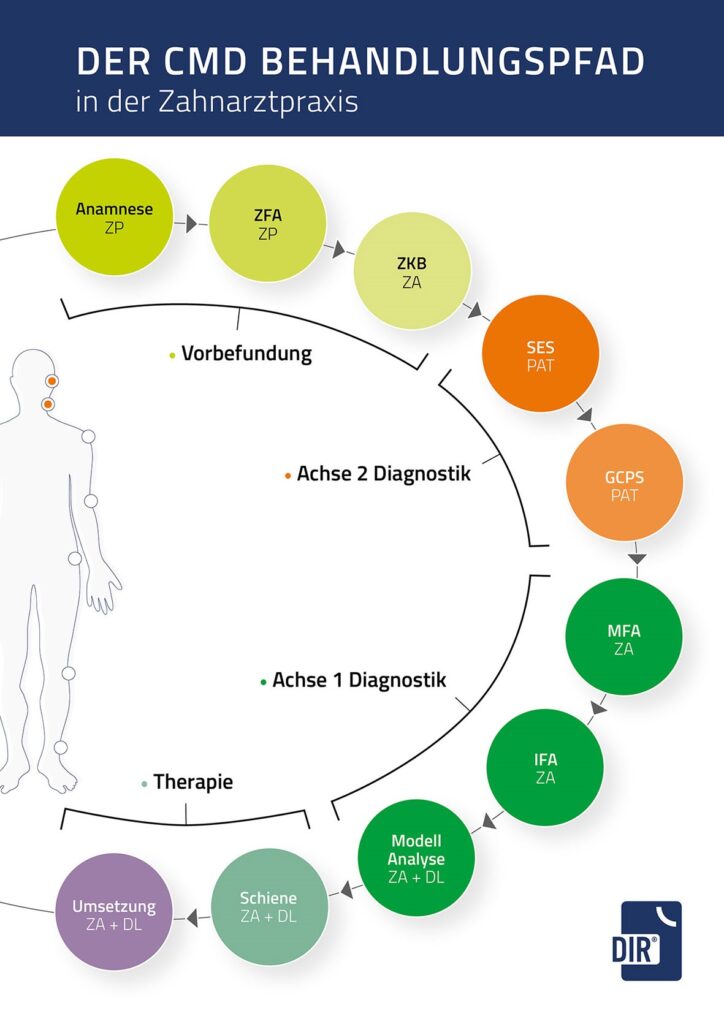
DIR® splint therapy
The corresponding DIR® splint therapy is planned on the basis of this result.
There are three different types of biomechanical DIR® splints.
The adjusted splint according to DIR® takes both condyles out of compression.
With the relief or relaxation splint according to DIR®, the two condyles are moved anteriorly or retrally by a small amount (1 to 2 mm).
With the DIR® reprogramming splint, the right or left condyle is rotated slightly and the contralateral condyle is rotated back.
The “Clinical-radiological study to evaluate the physiological condylar position in MRI” provided evidence of a centric position of the temporomandibular joint during DIR® splint therapy.
Wearing time of the DIR® splint
The respective DIR® splint is worn for at least six months with a follow-up measurement after three months.
The prerequisite for the implementation of the final prosthetic restoration, with continuous monitoring by the treating dentist, is that the patient is completely free of symptoms and that the lower jaw position has been successfully reprogrammed in the patient’s occlusal memory, as well as objective confirmation by means of a further control measurement.